Virtualization is a key component to building, testing and deploying software. In my experience, customers often struggle to test their application when their production and non-production systems vary. Customers also tend to spend too much time building test environments to match their production.
In the past, developers would use VirtualBox to build test environments for web applications and test scripts. With Vagrant’s release, developers are given the ability to import/export pre-configured environments and configure virtual machines using the Vagrantfile, and spin up additional machines easily and as needed. But these environments took time to set up when VirtualBox would crash.
Containers became the solution to this issue for developers. A container is a standardized unit of software that packages up code and all your dependencies so the application runs quickly and reliability from one computing environment to another. Docker provides container images, which are standalone and lightweight executable packages of software that include everything needed to run an application: code, run time, system settings, libraries and tools. But learning Docker is confusing and sometimes can take some work to connect ports to test your applications.
Utilizing tools like Vagrant and Docker below, I will show you how you can use these tools with VirtualBox to run on any Operating System (OS) on any machine you may have. Using this box, developers no longer have to concern themselves with worrying about OS and configuration mismatches between their local development environment and the production server.
In the demo below, these tools come together to create a powerful, disposable environment set up for a node.js application. The source code is included below if you want to make some changes to the environment yourself. This demo takes little to no prior knowledge on these tools and maybe just a little bit of knowledge in the command line.
Once you have completed the demo, Docker will host your application in a Vagrant provided box, running a Ubuntu virtual machine on Virtualbox. This environment is disposable, meaning it can be destroyed with the command ‘vagrant destroy’ at anytime, and rebuilt easily with ‘vagrant up’.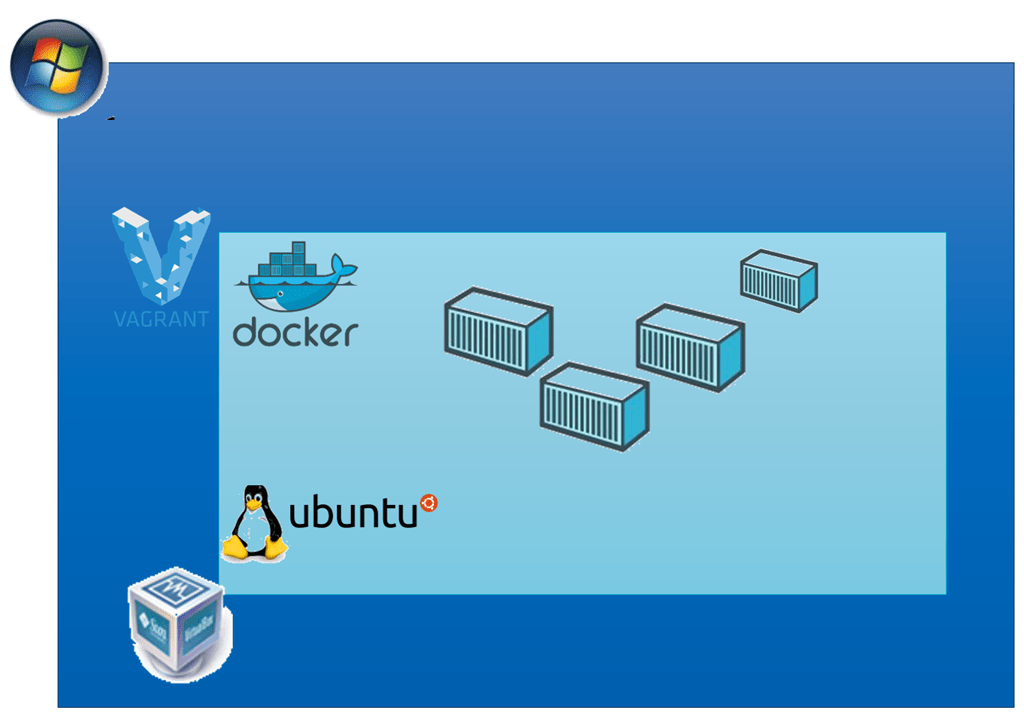
To get started, install Git, Docker, VirtualBox and Vagrant. You will need to have either a Windows, Linux or Mac operating system on your workstation for this box to work for you.
- Install Git: https://help.github.com/articles/set-up-git/
- Install Virtualbox: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
- Install Docker: https://docs.docker.com/install/
- Install Vagrant: https://www.vagrantup.com/downloads Make sure you install the Vagrant Host Updater also. https://github.com/cogitatio/vagrant-hostsupdater. Install the zip file for the vagrant-hostsupdater.
- Move to the directory where the vagrant-hostsupdater is installed, typically in the Downloads directory.
- Run $ vagrant install plugin vagrant-hostsupdater
- Run these commands
- $ git clone http://github.com/branmarshall21/Vagrant-Box.git
- $ cd Vagrant-Box
- $ vagrant up
- select this link……. http://localhost:8088
Your browser window should show a “hello world” message, which signifies that you have successfully built your first vagrant box!